fibrocytes vs fibroblasts|fibroblast marker genes : Tagatay Recent discovery of the fibrocyte, a circulating possible precursor cell to the tissue fibroblast in fibrosis, has raised issues regarding the characterization of .
webChoosing a selection results in a full page refresh. Press the space key then arrow keys to make a selection. Use left/right arrows to navigate the slideshow or swipe left/right if .
0 · what do myofibroblasts
1 · what are myofibroblasts
2 · size of human fibroblast
3 · gene signature of fibroblast
4 · fibroblast vs fibrocyte histology
5 · fibroblast marker genes
6 · fibroblast identification and heterogeneity
7 · difference between fibroblast and fibrocyte
8 · More
Remastered - STEAMUNLOCKED » Free Steam Games Pr.
fibrocytes vs fibroblasts*******Fibroblast and fibrocyte are two stages of a fiber-producing cell found in the connective tissues. Fibroblast and fibrocyte differ in . See more
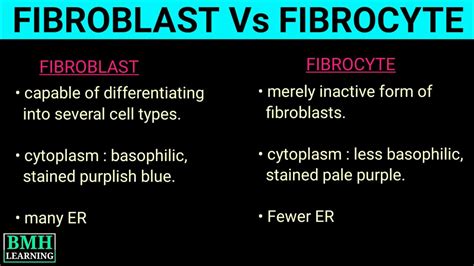
The inactive form of fibroblast is known as fibrocyte. Fibrocytes can be considered as mesenchymal cells with a small cytoplasm. . See more
fibrocytes vs fibroblasts fibroblast marker genesA fibroblast is an immature, fiber-producing cell found in the connective tissue. Fibroblasts are large flat cells, containing an oval shaped nucleus. They also consist of elongated structures, which protrude from the cell body. Therefore, the actual shape of a . See more Fibrocytes are hematopoietic-derived cells that directly contribute to tissue fibrosis by producing collagen following injury, during disease, and with aging. The lack .
Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Inactive fibroblasts, called 'fibrocytes', are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have less RER. Although disjointed and scattered when covering large spaces, fibroblasts often locally align in par.
Recent discovery of the fibrocyte, a circulating possible precursor cell to the tissue fibroblast in fibrosis, has raised issues regarding the characterization of .
Circulating and lung fibrocytes are increased during the pathogenesis of IPF and they are postulated to communicate with alveolar cells to cause epithelial to . Beyond gene markers, functional properties are the ultimate discriminator of shared vs. unique themes in fibroblast biology. In this section, we outline the shared .
Fibroblasts, the principal cell type of connective tissue, secrete extracellular matrix components during tissue development, homeostasis, repair and disease. .A fibrocyte is an inactive mesenchymal cell, that is, a cell showing minimal cytoplasm, limited amounts of rough endoplasmic reticulum and lacks biochemical evidence of .
Fibrocytes are monocyte-derived cells that have features of both macrophages and fibroblasts. Although their biology has come under study only recently, the existence of a.
Fibrocytes are hematopoietic-derived cells that directly contribute to tissue fibrosis by producing collagen following injury, during disease, and with aging. The lack .
Par conséquent, les fibrocytes produisent moins de protéines. Les cellules nées du sang, qui quittent le sang et pénètrent dans les tissus pour devenir des fibroblastes, sont également appelées fibrocytes. Les fibroblastes et les fibrocytes dans un tissuFigure 2.Purpose: This review highlights the roles of fibrocytes—their origin, markers, regulation and functions—including contributions to corneal wound healing and fibrosis. Methods: Literature review. Results: Peripheral blood fibroblast-like cells, called fibrocytes, are primarily generated as mature collagen-producing cells in the bone marrow. Fibrocytes are monocyte-derived cells that have features of both macrophages and fibroblasts. They are unique because they co-express hematopoietic and progenitor cell markers (CD45 and CD34 .Fibrocytes are mesenchymal progenitor cells presumed to be of monocyte origin that possess the tissue remodeling properties of tissue resident fibroblasts such as extracellular matrix production and α-SMA-related contractile properties, as well as the immunologic functions typically attributed to macrophages including production of cytokines .Fibroblasts. The normal heart is comprised of four major cell types; myocytes, endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells (within vessels) and the fibroblasts. The proportion of each cell types varies with species ( 1) but overall myocytes make up less than half of the cellular population of the heart. The fibroblasts make up a large portion of the .fibrocytes vs fibroblasts Wen-Hwa Lee. British Journal of Cancer (2024) In chronic infection, inflammation and cancer, the tissue microenvironment controls how local immune cells behave, with tissue-resident fibroblasts . Fibrocytes, which originate from bone marrow, can develop into different effector cells outside the circulation depending on the local tissue environment [1]. They can be identified by detecting the expression of CD34 and/or CD45 and collagen production [2]. Fibrocytes are important cells in the process of pulmonary fibrogenesis [3]. Extracellular matrix: Fibroblasts produce collagen and other proteins that make up the ECM. This is the network of fibers that support tissues in the body, such as the skin, organs, and blood vessels. Tendons and bones: The collagen protein produced by fibroblast cells is a critical component of cartilage (found in joints and between bones), . However, fibrocytes themselves produce a number of cytokine and growth factors 2, 37 that induce angiogenesis 37 or fibroblast hyperplasia 36 and promote the release of ECM molecules from resident . As well as being present as fibroblasts, these cells exist in an alternative state, as fibrocytes. Fibroblast is the term used to describe these cells when they are in an activated state. Fibroblasts were first described as a distinct cell type in 1858 by German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who called them “Spindelzelle des Bindegewebes” – “spindle-shaped cells of the connective tissue” (Virchow, 1858) (Figure 2A).The term “fibroblast” was first proposed by Ernst Ziegler to describe cells that produce new connective tissue upon .
Fibrocytes are circulating fibroblast-like cells in the vascular system that are derived from bone marrow stem cells (Bucala et al., 1994). “Fibrocyte” is a term sometimes ascribed to a relatively inactive fibroblast-like cell, whereas the term “fibroblast” designates a fully active cell as described throughout our review.
fibroblast marker genes Fibrocytes are circulating fibroblast-like cells in the vascular system that are derived from bone marrow stem cells (Bucala et al., 1994). “Fibrocyte” is a term sometimes ascribed to a relatively inactive fibroblast-like cell, whereas the term “fibroblast” designates a fully active cell as described throughout our review. Evidence for the Expansion of Pericyte-Derived Fibroblasts and Myofibroblasts in IPF. Given the heterogeneous sources of murine fibroblasts and myofibroblasts during fibrosis in the lung, it is likely that the changes observed in IPF might be due, in part, to an expansion and/or loss of comparable cell populations. It was assumed that fibrocytes give rise to fibroblasts upon wounding, and conversely that fibroblasts differentiate into fibrocytes during healing 10. Perhaps due to limited interest in the quiescent cells, the original meaning of fibrocyte was progressively lost and fibroblast adopted as the common name irrespective of its state of activity. Semantic Scholar extracted view of "Fibrocytes and Fibroblasts - where are we now." by S. Chong et al. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.105595 Corpus ID: 201716809 Fibrocytes and Fibroblasts - where are we now. @article{Chong2019FibrocytesAF, title={Fibrocytes .
Fibrocytes, a group of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells, were first described in 1994 as fibroblast-like, peripheral blood cells that migrate to regions of tissue injury. These cells are unique in their expression of extracellular matrix proteins concomitantly with markers of hematopoietic and monocyte lineage. The involvement of .1. Fibroblasts are easy to grow in culture. As mentioned, the main role of fibroblasts is the production of ECM, which provides support for connective tissues and serves to maintain structural integrity. Fibroblasts effectively create their own environment, and as such, they are simple and easy to grow in culture. 2.
Fibrocytes are circulating fibroblast-like cells in the vascular system that are derived from bone marrow stem cells (Bucala et al., 1994). “Fibrocyte” is a term sometimes ascribed to a relatively inactive fibroblast-like cell, whereas the term “fibroblast” designates a fully active cell as described throughout our review.
2 dias atrás · Filmes Online HD. Mad Max. Feb. 28, 2024. Movie. Harry Potter e o Prisioneiro de Azkaban. Feb. 28, 2024. Movie. Hooking Up. Feb. 28, 2024. Movie. Dupla .
fibrocytes vs fibroblasts|fibroblast marker genes